Retrocausal artificial intelligence in the plastics industry
Over the last decade, there have been several advances in the automation and digitalization of industrial processes, driven by technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI). However, a significant portion of the manufacturing sector continues to carry out many operations manually.
This happens even in companies that have high levels of investment and access to cutting-edge technologies. There are several reasons why manual labor continues. These include the high cost of implementing automation in certain processes and the complexity of the automation system required.
In addition, it is common for very similar products within the same industry to have part of their production fully automated, while the rest is still manual. In this case, the reasons are production volume and economic viability.
In other situations, local legislation or tax incentives, such as those offered in Free Trade Zones, favor companies that generate more jobs in the region. The result is that manual operations are maintained instead of investing in automation.
So, although technology has significantly transformed the industry landscape, the coexistence of manual and automated processes is a reality that reflects the complexity of business decisions, economic challenges and regulatory influences underway in the manufacturing industry.
Manual labor in the plastics industry
The plastics and polymers industry is a prominent segment. Among the various applications of plastic, products aimed at another strong and strategic sector stand out: civil construction. Pipes, fittings, conduits, conductors and insulators are examples of plastic products aimed at this segment.
Most of the manufacturing of these items tends to be automated, using injection molding machines, extruders and blow molding machines, for example. However, the assembly of the different components of a plastic product is still usually done manually. Among the steps that are still carried out manually by an operator are:
- removing burrs from products;
- fitting small plastic parts or parts made of other materials, such as rubber sealing rings or metal bushes;
- assembling products;
- packaging a set of items that make up the product.
How can artificial intelligence be applied to manual processes in the plastics industry?
Digitizing processes in the plastics industry can be done using computer vision and artificial intelligence tools. An excellent option is the Pathfinder platform, developed by Retrocausal and brought to the European market by Macnica ATD Europe. To implement it, there is no need to make intrusive changes to the existing infrastructure, layout or industrial processes.
This tool monitors workstations and identifies in real time whether the correct sequence of steps is being followed by the operator. This allows greater control over the quality of all items produced and facilitates decision-making.
By identifying metrics such as the time spent on each step and cycle and the items and steps with the highest number of errors, the platform allows managers and supervisors to quickly recognize incorrectly assembled products.
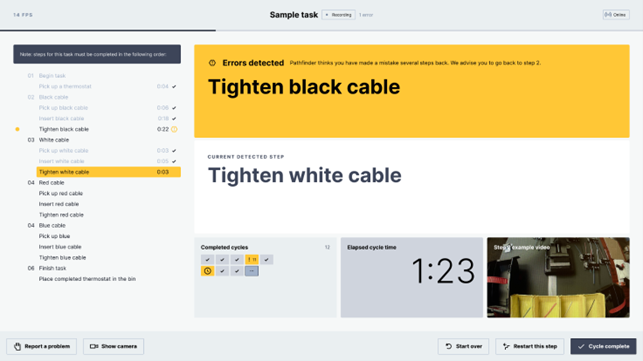
Display shown on Retrocausal's Pathfinder Apollo platform with operator alerts. Source: Retrocausal.
Avoiding these errors in manual production saves a lot of money, since small plastic items in the segment tend to have low added value, and a return or refund to the consumer can cost dozens of times its price. In addition, poor quality products damage the brand's image.
Benefits of applying Retrocausal's artificial intelligence to manual production
The plastics industry is increasingly investing in tools and technologies that enable operational efficiency, reducing costs and production defects. And Retrocausal's artificial intelligence solution is an excellent choice right now.
Here are the main benefits of the Pathfinder Apollo tool for manual production lines:
- Up to 10% increase in production;
- 60% reduction in assembly quality problems;
- 44% reduction in training time for new operators;
- improvement of the production process through metrics and statistics;
- greater control and management of activities;
- live feedback during training and orientation.
Do you have manual manufacturing processes in your industry and want to guarantee the quality of manually assembled products and find out about other solutions and technologies for Industry 4.0? Click here, contact us and find out about the best artificial intelligence solutions on the market.

